With a projected value of $145 billion by 2030, the large diameter pipe market is poised for significant growth, driven by rising investments in water management and infrastructure renewal. However, the applications of wide diameter tubes extend beyond these projects. Here Lauri Turunen, product manager for tubes at pultruded & pull-wound composites specialist Exel Composites, explores the versatility of wide tubes, how new materials are outperforming traditional ones, and where the future of tubes is heading.
Wide diameter tubes are defined as those with a diameter greater than 100mm and are designed to handle a variety of industrial applications due to their robust size and strength. These tubes are engineered to support substantial loads and resist external forces, making them crucial for projects that demand structural integrity.
In the construction sector, wide diameter tubes serve multiple functions, such as structural supports, utility poles, and fender systems in marina construction. Their load-bearing capacity ensures stability in structural applications and supports high-voltage equipment while withstanding environmental conditions like heavy rain and strong winds and currents.
In the oil and gas industry, these tubes are used as pipelines, effectively managing high pressure and flow rates associated with transporting fluids over long distances. This enables the safe and efficient delivery of oil, gas, and other liquids.
Additionally, wide diameter tubes play a vital role in robotics and military applications. They are used in large-scale masts and antennas, providing the strength and stability required for long-distance communication and surveillance. For mobile towers and other adjustable equipment, they serve as telescoping poles, maintaining structural integrity when extending or retracting, essential in dynamic environments.
Why pultruded composites?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, provide substantial benefits over traditional materials for wide-diameter tubes, particularly when manufactured using the pultrusion method.
This continuous production process involves drawing reinforcing fibers, such as glass or carbon, through a resin matrix and curing them in a heated die to create lightweight, durable profiles with exceptional precision. Pultrusion significantly reduces material waste and ensures consistent quality, making it an efficient and reliable solution for producing high-performance tubes.
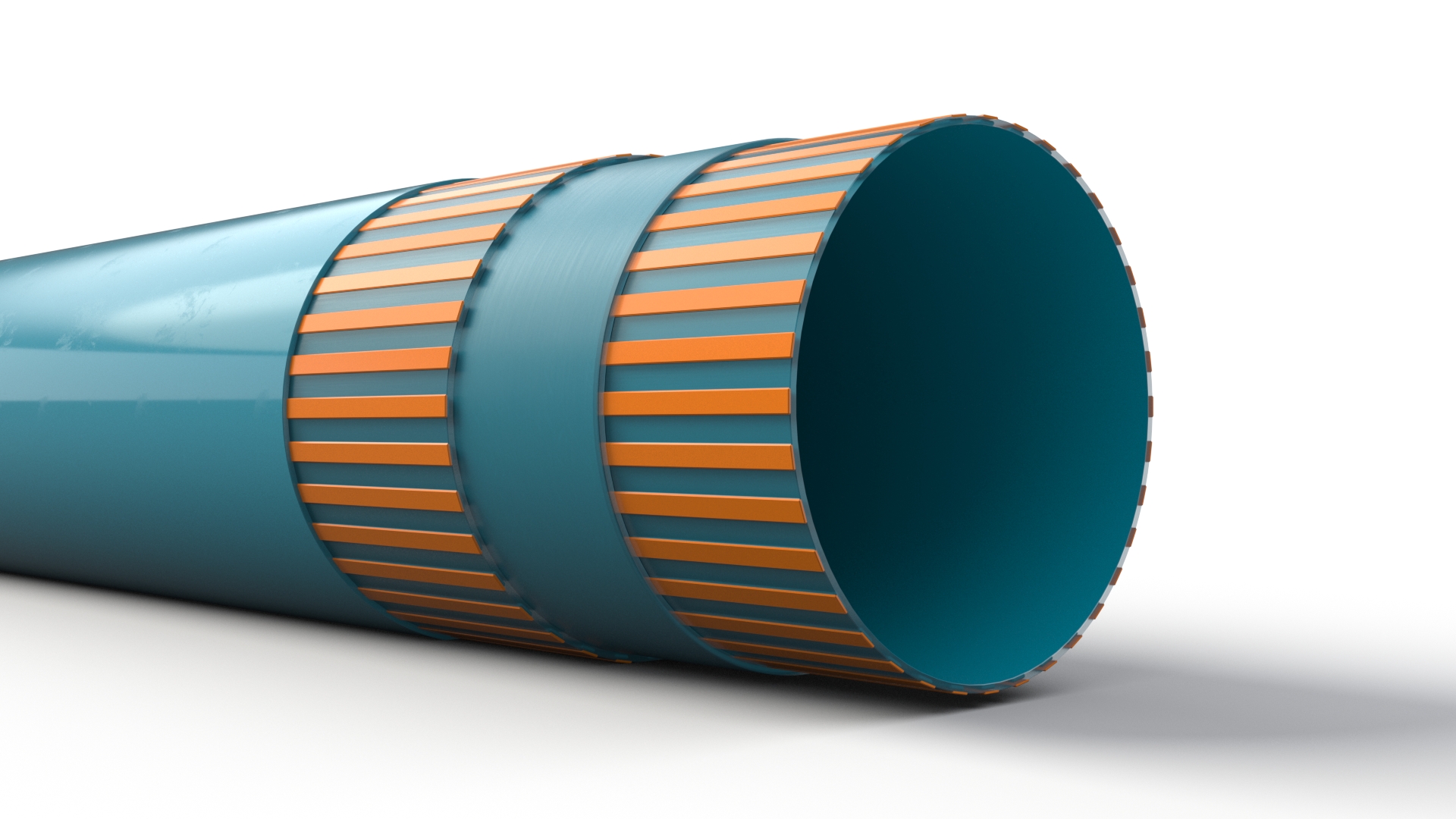
For instance, glass fiber has a density of around 2.5 g/cm3, approximately 75 per cent less than steel at 7.85g/cm3, despite possessing superior strength. This gives composites an edge over other materials. Although glass fiber may come at a higher material cost, its lighter weight makes it quicker to install and requires few personnel, ultimately lowering labor costs and speeding up project timelines.
A case in point is EasyStreet Systems, a company that uses and installs composite utility poles for smart infrastructure projects. By opting for lightweight composites, it can reduce the installation time, and the number of staff required, with many poles being installable by a single person. This not only lowers installation costs, but increases the speed of deployment, allowing more to be installed in the same time frame, enhancing overall revenue.
Composites also excel in corrosion resistance. In harsh marine environments, where wide diameter tubes might serve as structural support for piers, composites can have a service life that surpasses that of traditional materials like wood or steel, which can begin to corrode within five to ten years.
While building standards and codes account for the expected durability of these materials, composites can offer a longer lifespan, translating to lower maintenance and replacement costs compared to metals.

Future applications
The role of wide diameter composite tubes is set to expand significantly as demand for sustainable infrastructure solutions grows. Their high strength-to-weight ratio makes them ideal for applications such as pedestrian bridge supports or in the rehabilitation of existing structures, offering a durable and low-maintenance alternative to traditional materials.
In robotics, the use of wide diameter tubes in large-scale manipulators is expected to increase, with composites enabling the creation of lightweight yet robust structures. Similarly, in aerospace, these tubes could become integral to support structures for aircraft and spacecraft, contributing to weight reduction while maintaining strength.
As engineering embraces these innovations, wide diameter composite tubes are becoming essential across projects from water infrastructure to modern aerospace due to their strength and durability. To see how these advancements can impact your projects, visit www.exelcomposites.com/composite-solutions/composite-tubes/ and discover the benefits of composite materials.